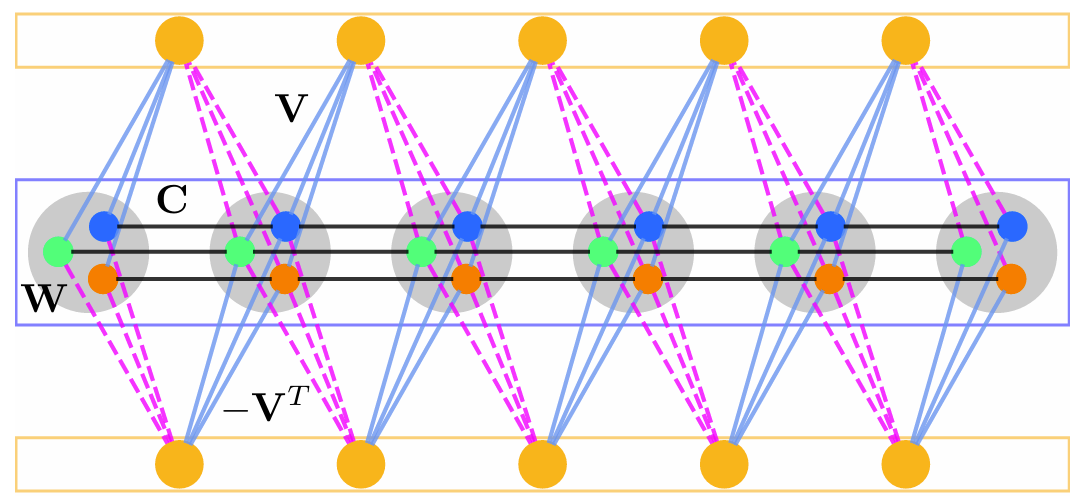
The reliable simulation of spin models is of critical importance to tackle complex optimization problems that are intractable on conventional computing machines. The recently introduced hyperspin machine, which is a network of linearly and nonlinearly coupled parametric oscillators, provides a versatile simulator of general classical vector spin models in arbitrary dimension, finding the minimum of the simulated spin Hamiltonian and implementing novel annealing algorithms. In the hyperspin machine, oscillators evolve in time minimizing a cost function that must resemble the desired spin Hamiltonian in order for the system to reliably simulate the target spin model. This condition is met if the hyperspin amplitudes are equal in the steady state. Currently, no mechanism to enforce equal amplitudes exists. Here, we bridge this gap and introduce a method to simulate the hyperspin machine with equalized amplitudes in the steady state. We employ an additional network of oscillators (named equalizers) that connect to the hyperspin machine via an antisymmetric nonlinear coupling and equalize the hyperspin amplitudes. We demonstrate the performance of such an equalized hyperspin machine by large-scale numerical simulations up to 10000 hyperspins. Compared to the hyperspin machine without equalization, we find that the equalized hyperspin machine (i) Reaches orders of magnitude lower spin energy, and (ii) Its performance is significantly less sensitive to the system parameters. The equalized hyperspin machine offers a competitive spin Hamiltonian minimizer and opens the possibility to combine amplitude equalization with complex annealing protocols to further boost the performance of spin machines.
[2507.12940] Equalized Hyperspin Machine
Phys. Rev. A 112, 053505 (2025)