Category: ERC-AdG HYPERSPIM
Hyperscaling in the Coherent Hyperspin Machine in PRL !
Classical and quantum systems are used to simulate the Ising Hamiltonian, an essential component in large-scale optimization and machine learning. However, as the system size increases, devices like quantum annealers and coherent Ising machines face an exponential drop in their success rate. Here, we introduce a novel approach involving high-dimensional embeddings of the Ising Hamiltonian and a technique called “dimensional annealing” to counteract the decrease in performance. This approach leads to an exponential improvement in the success rate and other performance metrics, slowing down the decline in performance as the system size grows. A thorough examination of convergence dynamics in high-performance computing validates the new methodology. Additionally, we suggest practical implementations using technologies like coherent Ising machines, all-optical systems, and hybrid digital systems. The proposed hyperscaling heuristics can also be applied to other quantum or classical Ising devices by adjusting parameters such as nonlinear gain, loss, and nonlocal couplings.
https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.017301
See arXiv post
Exponential improvement in combinatorial optimization by hyperspins
Classical or quantum physical systems can simulate the Ising Hamiltonian for large-scale optimization and machine learning. However, devices such as quantum annealers and coherent Ising machines suffer an exponential drop in the probability of success in finite-size scaling. We show that by exploiting high dimensional embedding of the Ising Hamiltonian and subsequent dimensional annealing, the drop is counteracted by an exponential improvement in the performance. Our analysis relies on extensive statistics of the convergence dynamics by high-performance computing. We propose a realistic experimental implementation of the new annealing device by off-the-shelf coherent Ising machine technology. The hyperscaling heuristics can also be applied to other quantum or classical Ising machines by engineering nonlinear gain, loss, and non-local couplings.
Hyperscaling in the coherent hyperspin machine
https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.02329

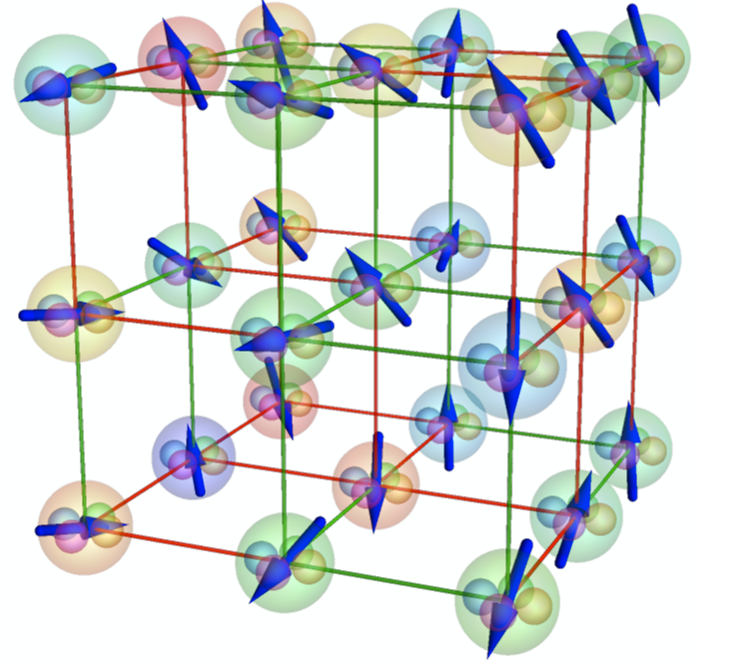
The Hyperspin Machine in Nature Communications !
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-34847-9
From condensed matter to quantum chromodynamics, multidimensional spins are a fundamental paradigm, with a pivotal role in combinatorial optimization and machine learning. Machines formed by coupled parametric oscillators can simulate spin models, but only for Ising or low-dimensional spins. Currently, machines implementing arbitrary dimensions remain a challenge. Here, we introduce and validate a hyperspin machine to simulate multidimensional continuous spin models. We realize high-dimensional spins by pumping groups of parametric oscillators, and show that the hyperspin machine finds to a very good approximation the ground state of complex graphs. The hyperspin machine can interpolate between different dimensions by tuning the coupling topology, a strategy that we call “dimensional annealing”. When interpolating between the XY and the Ising model, the dimensional annealing substantially increases the success probability compared to conventional Ising simulators. Hyperspin machines are a new computational model for combinatorial optimization. They can be realized by off-the-shelf hardware for ultrafast, large-scale applications in classical and quantum computing, condensed-matter physics, and fundamental studies.
See also The hyperspin machine: simulating QCD models and dimensional annealing

The hyperspin machine: simulating QCD models and dimensional annealing
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.16190
From condensed matter to quantum chromodynamics, multidimensional spins are a fundamental paradigm, with a pivotal role in combinatorial optimization and machine learning. Machines formed by coupled parametric oscillators can simulate spin models, but only for Ising or low-dimensional spins. Currently, machines implementing arbitrary dimensions remain a challenge. Here, we introduce and validate a hyperspin machine to simulate multidimensional continuous spin models. We realize high-dimensional spins by pumping groups of parametric oscillators, and study NP-hard graphs of hyperspins. The hyperspin machine can interpolate between different dimensions by tuning the coupling topology, a strategy that we call “dimensional annealing”. When interpolating between the XY and the Ising model, the dimensional annealing impressively increases the success probability compared to conventional Ising simulators. Hyperspin machines are a new computational model for combinatorial optimization. They can be realized by off-the-shelf hardware for ultrafast, large-scale applications in classical and quantum computing, condensed-matter physics, and fundamental studies.